# 栈的应用之逆序
在实际开发中,我们一旦遇到逆序的问题,可以想当然的先思考一下是否可以用栈进行处理。
# 两数相加 (opens new window)
# 描述
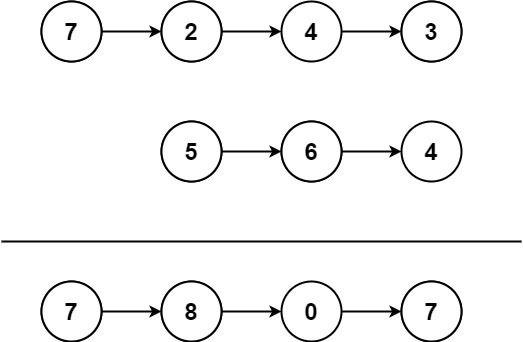
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
# 思路分析
因为是逆序,所以我们会想到用栈,分别遍历两个链表,用两个栈存储对应的节点,则问题转化为类似合并 2 个有序数组的问题。
# 算法实现
链表节点定义如下:
interface ListNode<T> {
next: ListNode<T> | null;
val: T;
}
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) {
const stack1 = [];
const stack2 = [];
let node1 = l1;
let node2 = l2;
while (node1 && node2) {
stack1.push(node1);
stack2.push(node2);
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next;
}
while (node1) {
stack1.push(node1);
node1 = node1.next;
}
while (node2) {
stack2.push(node2);
node2 = node2.next;
}
let needIncrease = false;
let newHead = null;
while (stack1.length && stack2.length) {
const num1Node = stack1.pop();
const num2Node = stack2.pop();
let val = num1Node.val + num2Node.val + (needIncrease ? 1 : 0);
needIncrease = false;
if (val >= 10) {
val = val - 10;
needIncrease = true;
}
const tempNode = {
val,
next: null,
};
if (!newHead) {
newHead = tempNode;
} else {
tempNode.next = newHead;
newHead = tempNode;
}
}
while (stack1.length) {
const num1Node = stack1.pop();
let val = num1Node.val + (needIncrease ? 1 : 0);
needIncrease = false;
if (val >= 10) {
val = val - 10;
needIncrease = true;
}
const tempNode = {
val,
next: null,
};
if (!newHead) {
newHead = tempNode;
} else {
tempNode.next = newHead;
newHead = tempNode;
}
}
while (stack2.length) {
const num2Node = stack2.pop();
let val = num2Node.val + (needIncrease ? 1 : 0);
needIncrease = false;
if (val >= 10) {
val = val - 10;
needIncrease = true;
}
const tempNode = {
val,
next: null,
};
if (!newHead) {
newHead = tempNode;
} else {
tempNode.next = newHead;
newHead = tempNode;
}
}
if (needIncrease) {
const tempNode = {
val: 1,
next: null,
};
tempNode.next = newHead;
newHead = tempNode;
}
return newHead;
};
# 无权图的单源最短路径
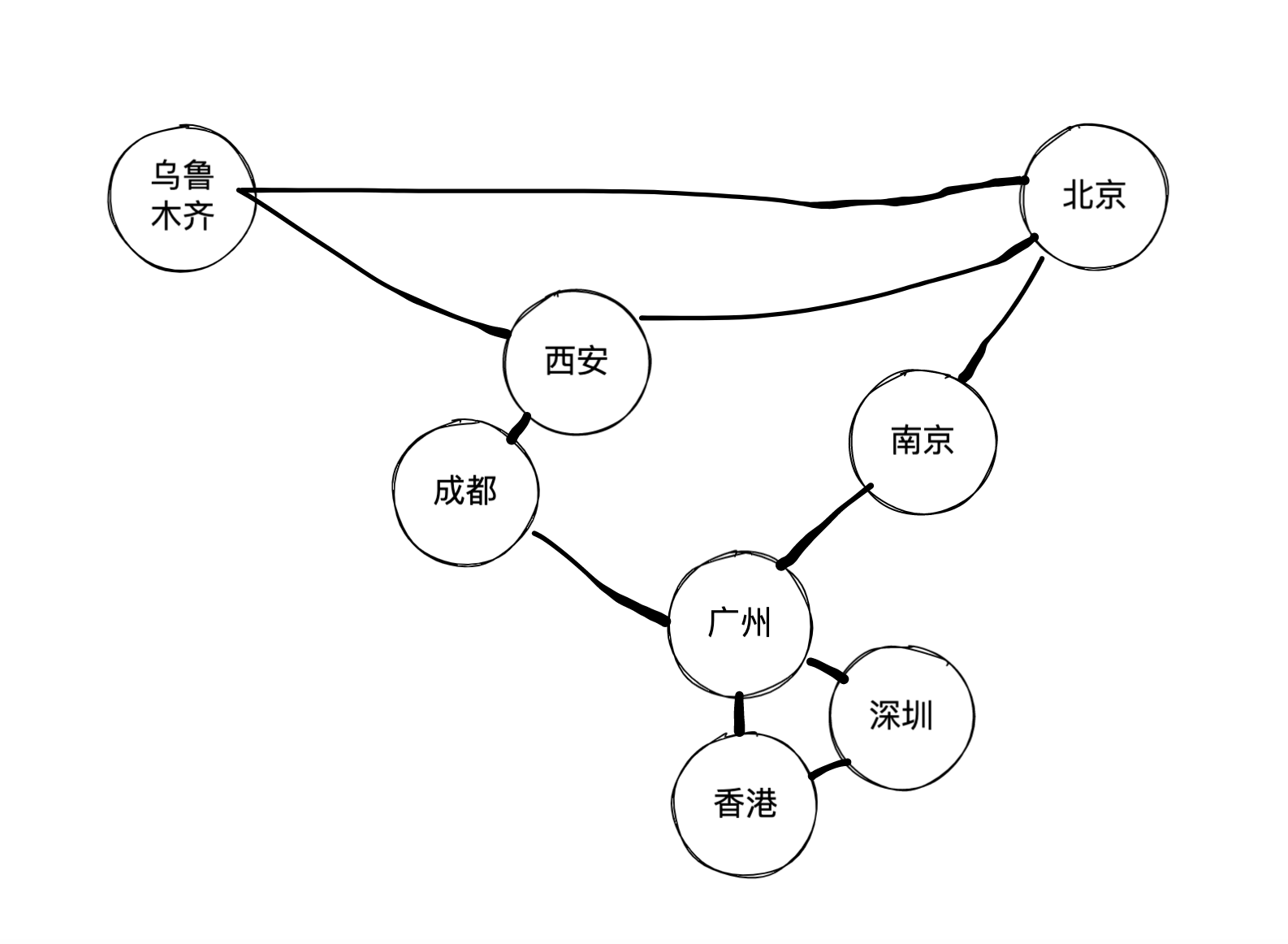
对于有这样的图:
假设我们用如下方式表示图:
class Edge {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 边的编号
*/
name;
/**
* 起始点
* @type {Vertex}
*/
from;
/**
* 终止点
* @type {Vertex}
*/
to;
}
class Vertex {
/**
* 城市名称
*/
cityName;
/**
* 邻接点
*/
siblings = [];
constructor(cityName) {
this.cityName = cityName;
}
}
class Graph {
vertexList = [];
edgeList = [];
addVertex(v) {
this.vertexList.push(v);
}
/**
* 增加边
* @param {Vertex} from
* @param {Vertex} to
*/
addEdge(from, to) {
const name = `${from.cityName}至${to.cityName}`;
const edge = new Edge(name);
this.edgeList.push(edge);
from.siblings.push(to);
to.siblings.push(from);
}
}
const g = new Graph();
const beijing = new Vertex("北京");
const nanjing = new Vertex("南京");
const guangzhou = new Vertex("广州");
const shenzhen = new Vertex("深圳");
const hongkong = new Vertex("香港");
const chengdu = new Vertex("成都");
const xian = new Vertex("西安");
const urumchi = new Vertex("乌鲁木齐");
/**
* 将城市加入到图中
*/
g.addVertex(beijing);
g.addVertex(nanjing);
g.addVertex(guangzhou);
g.addVertex(shenzhen);
g.addVertex(hongkong);
g.addVertex(chengdu);
g.addVertex(xian);
g.addVertex(urumchi);
/**
* 建立连接关系
*/
g.addEdge(beijing, nanjing);
g.addEdge(beijing, xian);
g.addEdge(nanjing, guangzhou);
g.addEdge(guangzhou, shenzhen);
g.addEdge(guangzhou, hongkong);
g.addEdge(hongkong, shenzhen);
g.addEdge(chengdu, guangzhou);
g.addEdge(chengdu, xian);
g.addEdge(urumchi, xian);
g.addEdge(urumchi, beijing);
/**
* 单源无权图的最短路算法
* @param {Vertex} start
* @param {Vertex} end
*/
function unweightedShortestPath(start, end) {
const queue = [];
const dist = new Map();
const path = new Map();
dist.set(start, 0);
queue.push(start);
while (queue.length > 0) {
let vertex = queue.shift();
for (let i = 0; i < vertex.siblings.length; i++) {
let adjoinVertex = vertex.siblings[i];
/* 若adjoinVertex未被访问过 */
if (typeof dist.get(adjoinVertex) === "undefined") {
/* 将这个点到start的距离更新 */
dist.set(adjoinVertex, dist.get(vertex) + 1);
/* 将这个点记录在S到adjoinVertex的路径上 */
path.set(adjoinVertex, vertex);
queue.push(adjoinVertex);
}
}
}
// 获取终点的最短路径长度
const distance = dist.get(end);
// 使用栈记住终点
const stack = [end];
let preVertex = path.get(end);
// 沿途处理从终点到起点所经过的路径
while (preVertex) {
stack.push(preVertex);
preVertex = path.get(preVertex);
}
// 经过逆序,得到了正确的路径
let via = "";
while (stack.length) {
const city = stack.pop();
via += "->" + city.cityName;
}
return { distance, path: via.replace(/(^->)|(->$)/g, "") };
}